As the name suggests, qualitative research design is the kind of research that accounts for the psyche of the target customers. It does not rely solely on numeric data. The readers can refer to the qualitative research design examples so that they can reach insights that can’t be quantified.
It is beneficial to researchers who want to gain knowledge about the beliefs, perceptions, and emotions of this target group. For example, in case you want to open a shoe store in a neighborhood, you must understand the demand and psychology of your target consumers. This is to ensure effective sales in addition to conducting quantitative research.
What is Qualitative Research Design?
Researchers can use qualitative research as a behavioral study to collect non-numeric data and gain an understanding of underlying reasons, opinions, and motivations. This type of research can uncover trends, thoughts, and opinions and help to dive deeper into the problem. Social sciences often use qualitative research, such as focus groups, interviews, and observations.
In-depth interviews, focus groups, and free-form questionnaires are just some of the methods utilized to probe this idea. With the goal of learning everything there is to know about the subject or theory. Used frequently to learn the inner workings of the minds of the people being studied.
Qualitative research can be used to augment quantitative research by scouting the motivations and experiences of the participants in relation to the study. The researchers can use this method to scout the motivations and experiences the participants harbor in relation to the study.
ALSO READ: An in-Depth Study of Simple Random SamplingQualitative Research Design Examples and Types
The researchers widely use this methodology to enrich their study. Broadly the following types of qualitative research design for a well-rounded insight.
Case Study
This is an in-depth investigation with respect to a single situation, event, or person. In simpler words, it is a comprehensive study and analysis of a person, place, or product.
Example: A business can employ a case study on a specific person to uncover their personality traits and create customer profiles or buyer personas. So that they can make or market the product better.
Ethnography
In ethnography, the systematic observation of a group in its natural environment allows researchers to reach conclusive evidence. It involves participant observation, interviews, and surveys. It provides a first-hand account of their psyche and motivations.
Example: An ethnographer could do an ethnography in a specific neighborhood to understand their behaviors and motivations with respect to the hypothesis.
Action Research
It involves exploring a problem, designing a solution, and then implementing the solution. We often use it to investigate issues related to educational practices or policy. Staying true to its name, action research focuses on taking action to reach substantial conclusions.
Example: A school could do an action research project to improve instruction or develop a new policy.
Focus Group
This involves gathering a group of people to examine a certain topic, issue, or product. Focus groups invite members to provide their insights on a new social media platform, often to explore public opinion or gain insight into a particular product or service.
Example: Let’s pretend a business is looking for client input while creating a new product. The company would then arrange a meeting with the participants, where a moderator would facilitate a discussion about the product.
Phenomenology
Here, we focus on the experiences of the participants who have lived a phenomenon. It aims to account for an individual perspective rather than a scientific one. With the aim of reaching a detailed description of the phenomenon through the lens of an individual.
Example: An individual aspect of the matter has immense significance in a diverse range of fields, such as psychology, sociology, education, and anthropology, which this study is employed for.
ALSO READ: Judgmental Sampling: An Effective but Less-talked Method
What are the Advantages of Qualitative Research?
As we’ve covered qualitative research examples and types. It is now time to look at the advantages of this research methodology.
- It provides a deep understanding of the subject matter and the underlying motivations of people.
- Researchers explore and explain why certain behaviors or attitudes occur.
- Helps to identify patterns in data analysis that may not be apparent in quantitative research.
- Allows for the exploration and interpretation of complex issues and relationships.
- Offer a fresh take on the subject or topic that quantitative studies have neglected.
- Tests the ideas and hypotheses generated by qualitative research.
- Gains a better insight into how people experience a particular situation or phenomenon, sincerely accounting for the individual aspect.
- It often takes more time and expense than qualitative research.
- Researchers can modify their approach as the study progresses because qualitative research is often more flexible and adaptive than quantitative research.
ALSO READ: Understanding Social Research: A Way To Cater To The Society Factors to Consider While Performing Qualitative Research
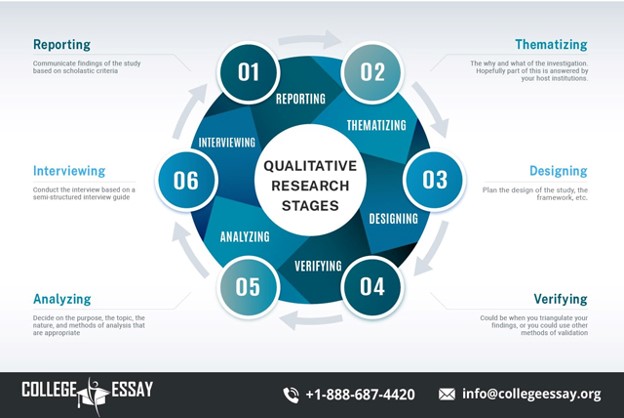
- Establish rapport: Establishing rapport with participants is essential for successful qualitative research. Which guarantees a trusting and relaxing setting for the research. This is to ensure participants express themselves without any hesitation.
- Observe behavior: Qualitative research involves observation of participants’ behavior. To provide valuable insights that are not apparent from their words.
- Analyze data: Thoroughly analyze the qualitative data to uncover the underlying meanings and patterns. Qualitative data analysis techniques such as coding and thematic analysis can help extract meaningful insights from the data.
- Communicate findings: The final step in conducting qualitative research is communicating the results to the relevant stakeholders. Ensure that findings are presented clearly and concisely to influence decision-making effectively.
Conclusion
Our piece on qualitative research design examples and types concludes here. Or you can go through the points to remember while employing this research method.
Furthermore, this method has relevance in modern times, when it is important to account for the individual factor. It has been noted that supplementing quantitative analysis with qualitative analysis is sure to enrich the insights.
Not Sure Where To Begin?
Explore our solutions to discover what is most important to your customers,
clients, and prospects. And best of all – it doesn’t take any coding!
Free Trial • No Payment Details Required • Cancel Anytime