Experimental design is a type of research design that involves manipulating conditions to observe how they affect a certain outcome. This design allows the researchers with an objective to determine the hypotheses and explore cause-and-effect relationships.
Whether in the fields of psychology, medicine, engineering, or beyond, experimental designs can provide valuable insights and answer important research questions. In this blog, we will delve deeper into experimental design, exploring its various forms, key components, and best practices.
So whether you’re a seasoned researcher or just starting out, read on to discover how experimental design can help you unlock new insights and advance your research goals.
What is Experimental Design?
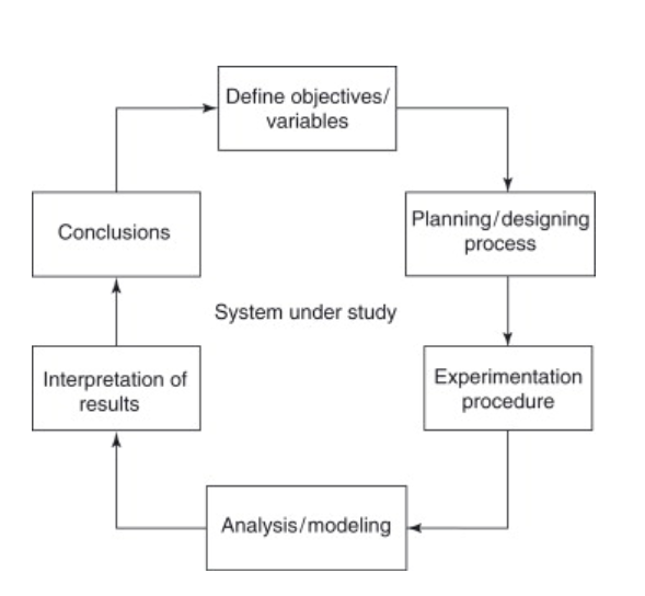
Experimental design is employed to investigate causal relationships between variables. In this process, an independent variable is manipulated to review the change in the dependent variables.
The experimental design is the framework that will be utilized to carry out the hypothesis. The plan lays forth the steps that need to be taken to achieve the intended outcomes.
Types of Experimental Design
One can select from the following types of experimental design to carry out their hypothesis.
1. Randomized Controlled Trial (RCT): This type of experimental design involves assigning participants to different treatment groups randomly. It aims to compare the effects of the treatments participants had.
2. Repeated Measures Design: It is to measure changes in behavior or outcomes over time by repeating a single treatment on the same group of participants.
3. Cross-Sectional Design: This type of experimental design includes juxtaposing different groups of participants at a single point in time.
4. Quasi-Experimental Design: It involves testing a treatment without random assignment of participants.
5. Single-Subject Design: This type involves testing a single participant over multiple trials. This is to measure changes in behavior or outcomes.
ALSO READ: Internal Validity: Making Your Survey Research More Beneficial Procedure to Create an Experimental Design
While carrying out experimental design, one can select from the various processes and frameworks available. It is crucial to religiously implement the following steps to carry out a successful and controlled experiment.
- Identify your Variables
- Frame a Hypothesis
- Construct Experimental treatments to operate independent variable
- Allocation of Subject to Groups
- Measurement of Dependent Variable
ALSO READ: The Right Time and Way To Do Quota SamplingIdentify Your Variable
The primary step is to identify the research question before identifying the variable for the experiment.
It will enable you to identify the data you need to collect and the types of variables you need to measure.
Then, you’re required to identify the independent and dependent variables:
- Researchers manipulate the independent variable in order to observe the effect on the dependent variable.
- The dependent variable is the one that is being measured in response to the manipulation of the independent variable.
Frame a Hypothesis
In experimental design, a hypothesis is a statement researchers make to predict the outcome of an experiment. With a hypothesis, you try to estimate or guess the experiment’s results.
Moreover, to construct a hypothesis, it is crucial to have an understanding of the problem you are trying to solve. Along with the variables that may be influencing the experiment. Hence, after identifying the variables, you can formulate a hypothesis that they can test.
For instance, here’s a hypothesis you might come up with if you were running an experiment to determine the efficacy of a new product:
“The new product will reduce the symptoms of the condition more effectively than the existing product.”
Construct Experimental Treatments
In order to determine the manipulation of the independent variable, researchers can use experimental treatments. Experimental design involves making deliberate changes to the independent variable, such as increasing or decreasing a treatment and randomly assigning participants to different groups to compare their outcomes.
By doing so, researchers can determine cause-and-effect relationships and draw meaningful conclusions from their data.
Design the treatments for each level of the independent variable. Further, this includes employing a myriad of stimuli, varying the duration of the treatment, or changing the intensity of the treatment.
ALSO READ: Choosing The Right Sources of Data For Analysis Allocation of Subjects to Groups
Researchers allocate subjects to groups in an experimental design based on the type and goal of the experiment they are conducting.
- In a randomized controlled trial (RCT), the allocation of subjects to groups is totally random.
- Subjects are allocated to groups in an observational study based on pre-existing characteristics or factors that may influence the experiment’s outcome.
- Case-control study, the allocation of cases and control would be on the basis of the presence or absence of a disease or condition.
- In a cross-over design, researchers allocate subjects sequentially to different groups to compare the effects of different interventions.
ALSO READ: Sampling Bias: A Threat to Accurate AnalysisMeasurement of Dependent Variable
Typically, researchers measure the dependent variable in an experimental design using various methods. These methods can include surveys, interviews, focus groups, observations, and experiments.
For instance, a rating scale or a set of questions about the subject could measure the dependent variable in a survey.
Researchers can measure the dependent variable by observing the subjects’ behavior when conducting an observational experiment. In a focus group, the dependent variable analyzes the conversations and interactions between participants.
Finally, researchers can measure the dependent variable using various tests or measurements in an experiment.
Experimental Design Psychology
Experimental design psychology is the field of psychology that focuses on employing experimental designs to help their research. Therefore, it involves utilizing different methods, such as randomized controlled trials, to study behavior.
This research gains a better understanding of the psychological processes at work. For the same reason, to frame effective treatments and interventions to help the participants. The experimental design and psychology fulfill the following purposes:
- Examining the effects of interventions or treatments.
- Understanding the process of acquired or modified behavior.
- Assessing the effectiveness of interventions or treatments.
- Studying the natural course of behavior over time.
- Comparing different groups or individuals.
Conclusion
Experimental design is an essential tool to help understand and conclude different hypotheses. It helps us to design experiments to answer questions, identify relationships, and make predictions.
With meticulous planning and an understanding of the variables involved, one can gain valuable insights and make meaningful progress in their research.
Not Sure Where To Begin?
Explore our solutions to discover what is most important to your customers,
clients, and prospects. And best of all – it doesn’t take any coding!
Free Trial • No Payment Details Required • Cancel Anytime