Imagine you have a favorite ice cream shop where you regularly enjoy delicious scoops of creamy goodness. Now picture the sadness you feel when you find out they’ve closed down or when you discover a new place that steals your heart.
That’s a little taste of customer churn.
It’s when customers stop doing business with a company, either by canceling their subscription or moving on to a competitor. It’s like losing a sweet, loyal friend in the ice cream world.
Customer churn is a critical concern for businesses across various industries. Let’s delve into this concept, explore its causes and consequences, and discuss effective strategies to mitigate and prevent it.

Why is Customer Churn Important?
The phenomenon of customer churn refers to customers discontinuing their relationship with a company, which can have significant negative impacts on revenue and growth. This churn is important for many reasons:
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): CLV is the overall value a customer shows to a business over their entire relationship. Decreasing churn means extending customer relationships and increasing their lifetime value. We can also maximize the return on investment by acquiring and serving customers.
- Revenue Impact: Customer churn directly affects a company’s revenue. When customers leave, it means lost sales and potential future revenue. By understanding and addressing churn, businesses can mitigate financial losses and work towards retaining valuable customers.
- Reputation and Brand Image: If customers are leaving due to dissatisfaction or poor experiences, it can spread through word-of-mouth or online reviews, damaging the company’s credibility and making it harder to attract new customers. Thus, reflecting negatively on a company’s reputation and brand image.
- Cost of Acquisition: Acquiring new customers can be costly. When existing customers churn, businesses have to invest more resources in marketing, sales, and advertising to replace them. By reducing churn, businesses can allocate those resources towards retaining and growing their current customer base, optimizing their cost of acquisition.
- Feedback and Improvement: Churn provides valuable insights into customer satisfaction, product/service quality, and areas for improvement. By analyzing churn patterns and reasons for customer departure, businesses can identify weaknesses and make necessary changes to enhance their offerings. Other aspects are customer experience, and overall satisfaction, leading to higher customer retention rates.
ALSO READ: Customer Experience in the Digital Age: Opportunities and Challenges| Consequences of Customer ChurnThere are severe implications for a business due to customer churn, including: Decline in revenue and profitabilityDecreased customer lifetime valueDamage to brand reputationIncreased customer acquisition costsLoss of market share |
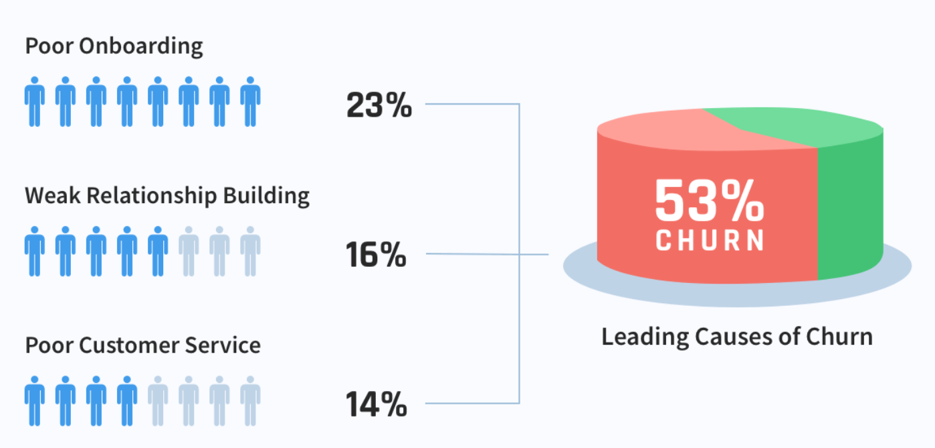
Common Causes of Customer Churn
- Poor Customer Experience: Dissatisfaction with product quality, customer service, or overall experience can drive customers away.
- Lack of Engagement: When customers feel disconnected or disengaged from a brand, they are more likely to churn.
- Competitor Influence: Aggressive marketing, better pricing, or superior offerings from competitors can tempt customers to switch.
- Pricing and Value Perception: If customers perceive a lack of value in relation to the price they pay, they may churn.
Changing Customer Needs: As customer preferences evolve, failing to adapt products and services can lead to churn.
How to Measure Customer Churn
To measure customer churn, you can follow these steps:
- Determine the period: Set a time frame for tracking churns, such as a month or a quarter.
- Calculate the churn rate: Subtract the total number of customers at the start from the number of customers lost over that time.
- Define churn criteria: Establish clear criteria for what constitutes a churned customer, such as cancellation of a subscription or not purchasing within a specific timeframe.
- Track customer data: Collect and analyze data on customer behavior, engagement, and transactions to accurately identify churned customers.
- Monitor over time: Regularly review and compare churn rates over different periods to identify trends, patterns, and potential factors influencing customer churn. This helps in developing strategies to reduce churn and improve customer retention.
Formula & Calculation
Churn Rate = (Number of customers lost over time ÷ the total amount of customers from the start) x 100%
Imagine you have a business with 1,000 customers at the beginning of the month. During that month, 100 customers decide not to continue using your product or service.
To figure that out, divide the number of customers who left (let’s say 100) by all customers at the start of the month (let’s say 1000).
Then, you multiply that result by 100% to get the percentage. In this example, the churn rate would be 10%, meaning that 10% of your customers decided to leave during that month.
=(100 customers lost ÷ 1000 total customers) x 100% = 10% churn rate
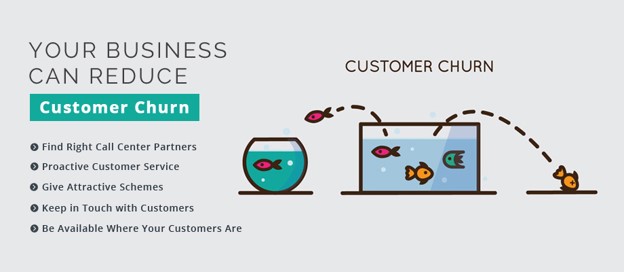
ALSO READ: How to Measure Customer Satisfaction: Tools and TechniquesStrategies to Reduce Customer Churn
- Enhance Customer Experience: Focus on delivering exceptional service, addressing pain points, and ensuring customer satisfaction.
- Build Strong Relationships: Foster personalized relationships with customers through effective communication and engagement.
- Personalization and Tailored Offerings: Provide personalized recommendations and offerings to meet individual customer needs. You can use several methods like surveys, interviews, or even a group discussion.
- Constant Product Improvement: Based on customer feedback, continuously review and improve your goods and services.
Difference Between Voluntary Churn and Involuntary Churn
It is essential to differentiate between voluntary churn (customer-initiated) and involuntary churn (external factors like credit card expiration).
Here’s a table comparing voluntary churn (customer-initiated) and involuntary churn in the business context:
| Voluntary Churn | Involuntary Churn | |
| Definition | When a person decides to leave or terminate their relationship at their own will. | When a person is forced to leave, the relationship ends due to circumstances beyond their control. |
| Decision-Maker | The person decides to initiate the churn. | Someone else makes the decision. Such as an employer or external factors. |
| Reasons | Personal choice, dissatisfaction, finding a better opportunity, or change in the circumstances. | Layoffs, company downsizing, business closures, or relocation. |
| Control | The person has control over the decision to churn and the timing of it. | The individual has little to no influence over the decision and the timing of the churn. |
| Impact | The person may have considered alternatives, evaluated options, and made a conscious decision. | The person may feel uncertainty due to the unexpected nature of the churn. |
| Emotional State | The person may experience a mix of emotions, such as excitement, relief, sadness, or nervousness about the change. | The person may experience emotions such as shock, disappointment, frustration, or anxiety about the situation. |
| Outcome | The person seeks new opportunities, embarks on a new journey, or transitions to a different phase of their life. | The person may need to adapt to new circumstances, seek new employment, or face challenges arising from the involuntary churn. |
In a nutshell, voluntary churn is when a person makes a conscious decision to leave or end a relationship. At the same time, involuntary churn happens when circumstances beyond their control force them to leave. Both types of churn can have different emotional and practical implications for the individual experiencing them.
Conclusion
Customer churn is a critical concern that businesses must address to ensure sustainable growth and success. Remember, proactive retention efforts are key to preserving customer loyalty and maximizing business profitability.
FAQs
What is an acceptable churn rate?
The acceptable churn rate varies depending on the industry and business model. However, generally, a lower churn rate is desirable. It’s important to monitor industry benchmarks and strive to keep your churn rate below the average for your sector.
How can businesses identify at-risk customers?
By analyzing customer behavior and engagement metrics, businesses can identify warning signs of potential churn. These may include decreased activity, a lack of interaction, or complaints.
Should businesses focus more on customer acquisition or retention?
While customer acquisition is vital for growth, customer retention is equally important. Typically, it is less expensive to keep current customers than to find new ones.
How can businesses win back churned customers?
Implementing a well-designed win-back strategy can be effective in re-engaging churned customers. This may involve personalized outreach, special offers or discounts, and addressing the reasons for their initial churn. Active listening, demonstrating improvements, and providing a compelling value proposition can help regain their trust and business.
Is it possible to prevent all instances of customer churn?
While it’s challenging to eliminate churn entirely, businesses can take proactive measures to minimize it. Businesses can create stronger customer relationships by delivering exceptional experiences and continuously evolving to meet their expectations. Thus reducing the likelihood of churn.

