Did you know that market segmentation dates back to the 1920s? It was first introduced by a Harvard professor named Wendell Smith. He used this concept to help tobacco companies identify target audiences based on their smoking habits.
Since then, market segmentation has developed and turned into a vital tool for businesses. Understanding consumers is the most important factor in running a successful company.
There are several types of market segmentation, including demographic, psychographic, behavioral, and geographic segmentation.
This blog will discuss geographic segmentation, which separates the market according to geographical variables such as location, region, climate, or population density.
Geographic Segmentation: What is it?
| Geographic segmentation is a type of marketing segmentation technique that involves breaking up an audience into various groups according to their geographic location, such as their city, state, region, or postal code. |
This kind of segmentation can offer insightful information about various geographic areas’ purchasing patterns and preferences, enabling more focused and successful marketing initiatives.
ALSO READ: Market Segmentation: Definition, Types, And Real-World Use CasesAdvantages of Geographic Segmentation
Here are some benefits of geographic segmentation:
- Focused Efforts: With this segmentation, you can successfully use location-specific keywords and know the demands. If you have a small budget or believe in creating awareness in a specific area, this is very helpful.
- Boost Communication: Every area has different needs, shopping preferences, and business practices. Talking to the population within regions and communities is considered during segmentation. With this kind of insight, you can proceed confidently and guarantee a high engagement level.
- Go Local: Consider your customers to be local businesses and treat them as such. Geographic segmentation is an essential marketing tactic for any business that offers services that vary by region due to climatic variations.
- Easy to Carry Out: Geographic segmentation is easier to carry out than other types of segmentation, such as demographic, psychographic, or behavioral. Finding someone’s location is much simpler than figuring out what makes them tick psychologically or what their tendencies are.
- Insightful Information: This segmentation can offer insightful information about various geographic areas’ purchasing patterns and preferences, enabling more focused and efficient marketing initiatives.
Companies selling products that climatic changes or regional customs may impact will find it most helpful. Your marketing efforts can be directed to the appropriate areas by routinely updating your segmentation.
ALSO READ: Why is Geographical Segmentation Important for Marketing?Factors of Geographic Segmentation
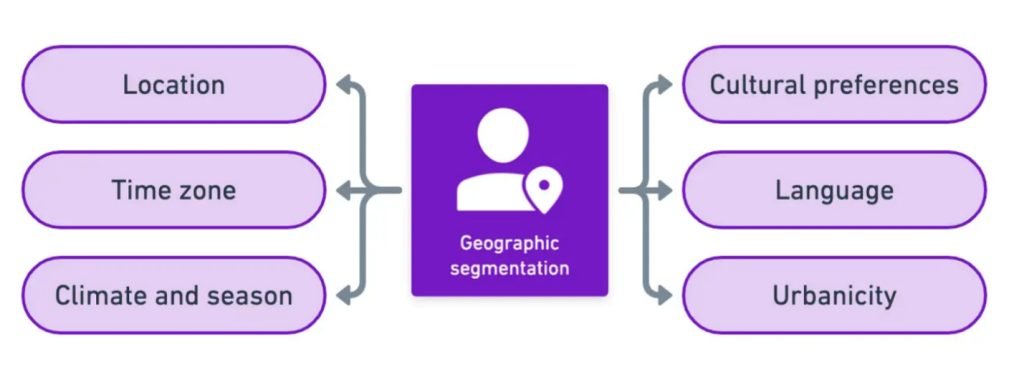
- Physical Positioning: The basis for geographic segmentation is the geographic units themselves. This includes nations, states, cities, and even neighborhoods.
- Climatic Conditions: Would you buy jackets in the summer? Segmenting your product or service according to the climate will help you determine what works and when.
For example, a clothing shop in India would stock up on dresses and slippers during the summer season rather than jackets and boots. Businesses should offer different products depending on the weather or season where a customer lives.
- Cultural Aspects: Every region has different needs, shopping preferences, and business practices. For example, at Western funerals, everyone wears black. Whereas, in the eastern parts of the world, white is worn. How people communicate within regions and communities is taken into account during geographic segmentation.
- Population: Geographic segmentation can also be based on population. For example, a luxury handbag company would not set up a shop in a rural area. In rural areas, needs and wants are restricted to basic amenities like food, shelter, clothing, etc.
- Communication: Segment the population based on what language they speak and understand. For example, advertising a cold drink on an English news channel would be made in English. Compared to an ad in a Hindi movie, it would be in Hindi.
McDonald’s: Classic Example of Geographic Segmentation
A real-life example of geographic segmentation based on location is McDonald’s. The fast-food chain has implemented highly successful approaches. It tailors its menu offerings and promotional campaigns to specific geographic segments.
For instance, McDonald’s adapts its menu in countries with diverse regional preferences. They focus on catering to local tastes and cultural preferences.
In India, a significant portion of the population practices Hinduism and abstains from consuming beef. McDonald’s offers a wide range of vegetarian options, like the McAloo Tikki burger and McVeggie burger.
This localized menu approach aligns with the dietary preferences and religious considerations of the Indian market. Thus, demonstrating the effectiveness of geographic segmentation.
Another example can be observed in the marketing efforts of McDonald’s in different climates. In hotter regions or during summer seasons, McDonald’s often introduces limited-time menu items. These include refreshing drinks, ice cream, and salads.
With this, they are targeting customers seeking lighter and cooler options. In colder regions or during winter seasons, the menu may focus more on warm and hearty items like soups, hot beverages, and comfort foods. This adaptation to local climates allows McDonald’s to cater to regional preferences and increase customer satisfaction.
These examples highlight how McDonald’s effectively implements geographic segmentation based on location.
By adapting menu offerings, marketing strategies, and promotions to cater to different geographic segments’ unique preferences and characteristics, McDonald’s can successfully connect with local consumers and create a more personalized and engaging experience.
ALSO READ: Popular Data Collection Methods To Draw Meaningful ConclusionsFAQs
How can geographic segmentation impact marketing effectiveness?
Understanding regional subtleties and cultural differences can help businesses produce more relevant and targeted marketing strategies. This results in higher engagement, increased customer satisfaction, and improved conversion rates.
What data sources are commonly used for geographic segmentation?
Businesses often rely on demographic data, customer addresses, zip codes, geolocation technology, etc. This is necessary information for effective geographic segmentation.
Are there any limitations to geographic segmentation?
While geographic segmentation provides valuable insights, it may oversimplify consumer behavior. This assumes that all individuals within a specific location are homogenous. Other segmentation factors, such as psychographics or behavior.
How can businesses overcome the challenges of geographic segmentation?
To overcome challenges, businesses can combine geographic segmentation with other segmentation approaches.
For example, demographic or psychographic segmentation to create more nuanced and targeted strategies. Regular data analysis and keeping up with market trends can also help refine the efforts.
Not Sure Where To Begin?
Explore our solutions to discover what is most important to your customers,
clients, and prospects. And best of all – it doesn’t take any coding!
Free Trial • No Payment Details Required • Cancel Anytime


