In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, the emergence of telehealth has revolutionized patient care, offering unprecedented access and convenience. Teletherapy, a subset of telehealth, has particularly gained traction, offering therapy sessions remotely through various digital platforms. But how does teletherapy compare to traditional face-to-face patient care? In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the nuances of telehealth versus in-person care, examining their significance, costs, benefits, and best practices across health and social care domains.
Defining Teletherapy
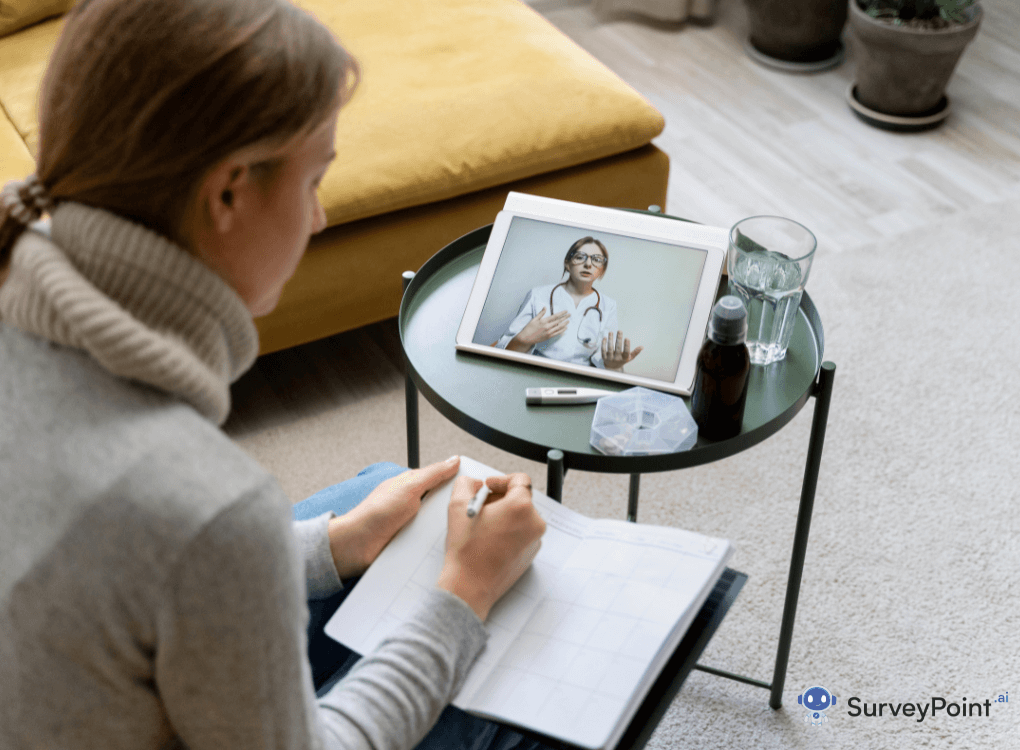
Teletherapy encompasses therapeutic services provided remotely through telecommunications technology. It enables therapists and clients to engage in counseling sessions via video conferencing, phone calls, or messaging platforms, eliminating geographical barriers and offering greater flexibility.
Telehealth vs. Face-to-Face Patient Care: Significance
Telehealth and face-to-face patient care are both integral components of the healthcare ecosystem, each serving unique purposes and addressing different aspects of patient needs. Understanding the importance of both modalities is crucial for optimizing healthcare delivery and ensuring patient-centered care. Let’s explore why telehealth and face-to-face patient care are important:
- Accessibility: Telehealth plays a critical role in improving access to healthcare services, especially for individuals living in rural or underserved areas. By leveraging digital communication technologies, telehealth eliminates geographical barriers and enables patients to receive medical care remotely. This is particularly beneficial for patients with limited mobility, transportation challenges, or those residing in areas with a shortage of healthcare providers. On the other hand, face-to-face patient care ensures accessibility to comprehensive medical evaluations, diagnostic tests, and hands-on treatments that may not be feasible through remote consultations alone.
- Convenience: Telehealth offers unparalleled convenience for patients by providing access to healthcare services from the comfort of their homes or workplaces. This convenience is especially valuable for individuals with busy schedules, mobility limitations, or chronic illnesses that require frequent monitoring and follow-up care. Telehealth eliminates the need for lengthy commutes, waiting room times, and time off work associated with traditional face-to-face appointments. However, face-to-face patient care remains essential for certain medical procedures, physical examinations, and interventions that cannot be effectively conducted remotely.
- Continuity of Care: Both telehealth and face-to-face patient care contribute to maintaining continuity of care for patients, ensuring seamless transitions between different healthcare settings and providers. Telehealth facilitates ongoing communication and follow-up appointments, allowing patients to stay connected with their healthcare providers between in-person visits. This continuity of care is particularly valuable for managing chronic conditions, coordinating multidisciplinary treatment plans, and promoting patient engagement in self-care activities. Face-to-face interactions, on the other hand, foster trust, rapport, and personalized connections between patients and healthcare providers, enhancing the patient experience and facilitating collaborative decision-making.
- Cost-effectiveness: Telehealth has the potential to lower healthcare costs by reducing expenses related to transportation, facility overheads, and administrative burdens associated with traditional healthcare delivery models. By leveraging telecommunication technologies, healthcare providers can deliver timely medical interventions, preventive care, and disease management services at a lower cost compared to in-person visits. However, it is important to balance cost considerations with the quality of care and patient outcomes when integrating telehealth into healthcare delivery systems.
- Patient Preferences: Recognizing and accommodating patient preferences is essential for delivering patient-centered care. While some patients may prefer the convenience and flexibility of telehealth consultations, others may value the personal interaction and hands-on care provided during face-to-face appointments. Healthcare providers should offer patients a choice between telehealth and in-person care whenever feasible, considering individual preferences, clinical needs, and cultural considerations.
In summary, both telehealth and face-to-face patient care play indispensable roles in modern healthcare delivery, offering complementary solutions to address the diverse needs of patients. By leveraging the strengths of both modalities and integrating them into comprehensive care delivery models, healthcare providers can optimize access, convenience, continuity of care, cost-effectiveness, and patient satisfaction across diverse patient populations.
Cost of Telehealth vs. In-Person Care
One of the key considerations in comparing telehealth and in-person care is the associated costs. Telehealth often proves to be more cost-effective for both patients and healthcare providers. It reduces expenses related to transportation, parking, and time off work, making healthcare more accessible to economically disadvantaged populations. However, the initial setup costs for telehealth infrastructure and technology may pose financial challenges for healthcare institutions.
Best Practices in Utilizing In-Person and Telehealth Services
Optimal healthcare delivery involves integrating both in-person and telehealth services judiciously. While telehealth excels in providing routine check-ups, follow-up appointments, and mental health counseling, certain medical conditions necessitate in-person assessments and interventions. Collaborative care models that combine telehealth with traditional in-person visits ensure comprehensive and holistic patient care.
Examples of Using Face-to-Face Care and Telehealth Services
Examples of utilizing both face-to-face care and telehealth services across various healthcare domains illustrate the versatility and effectiveness of these modalities in delivering comprehensive patient care:
Primary Care Consultations:
- Face-to-Face Care: Routine physical exams, vaccinations, and screenings for conditions like hypertension or diabetes often require in-person visits to assess vital signs, conduct physical examinations, and perform diagnostic tests.
- Telehealth Services: Follow-up appointments for medication management, reviewing lab results, or discussing minor ailments like colds or allergies can be efficiently conducted via telehealth platforms, minimizing the need for in-person visits.
Mental Health Counseling:
- Face-to-Face Care: Initial psychiatric evaluations or therapy sessions involving intensive interventions may necessitate in-person interactions to establish rapport and ensure a supportive environment.
- Telehealth Services: Ongoing therapy sessions, counseling for anxiety, depression, or stress management, and psychiatric medication management can be effectively delivered through telehealth, offering convenience and accessibility for patients.
Chronic Disease Management:
- Face-to-Face Care: Comprehensive assessments, disease education, and lifestyle counseling for chronic conditions such as heart disease, asthma, or arthritis often require face-to-face consultations to develop personalized treatment plans and address complex medical needs.
- Telehealth Services: Remote monitoring of vital signs, medication adherence, and symptom tracking can be facilitated through telehealth platforms, enabling proactive management of chronic diseases and timely interventions to prevent complications.
Specialist Consultations:
- Face-to-Face Care: Referrals to specialists for complex medical conditions, surgical evaluations, or procedures like biopsies or joint injections typically involve in-person consultations to conduct specialized assessments and coordinate multidisciplinary care.
- Telehealth Services: Follow-up visits with specialists for medication adjustments, post-operative care, or discussing treatment options can be efficiently conducted via telehealth, reducing travel burdens for patients and facilitating ongoing communication between primary care providers and specialists.
Emergency and Urgent Care:
- Face-to-Face Care: Acute medical emergencies, traumatic injuries, or severe symptoms requiring immediate intervention necessitate in-person evaluation and treatment in emergency departments or urgent care clinics.
- Telehealth Services: Triage services, initial assessments for non-life-threatening conditions, and follow-up consultations for minor injuries or illnesses can be provided through telehealth platforms, offering convenient access to medical advice and reducing overcrowding in emergency rooms.
These examples highlight the complementary roles of face-to-face care and telehealth services in delivering comprehensive, patient-centered healthcare. By leveraging the strengths of both modalities and tailoring care delivery to individual patient needs, healthcare providers can optimize resource allocation, enhance access to care, and improve health outcomes across diverse patient populations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between telehealth and in-person care should be guided by the specific needs of patients and the nature of their medical conditions. While telehealth expands access and offers convenience, in-person care ensures comprehensive evaluation and hands-on treatment when necessary. By leveraging the strengths of both modalities, healthcare providers can deliver patient-centered care that addresses the diverse needs of individuals across health and social care settings.
This blog aims to illuminate the nuances of telehealth and in-person care, empowering readers to make informed decisions about their healthcare options in an increasingly digitalized world. As technology continues to advance and healthcare delivery models evolve, striking a balance between innovation and tradition is paramount in ensuring equitable and effective healthcare for all.