Product positioning is an essential procedure that companies, whether fledgling startups or established corporations, must undertake to bring their product to the market. This complex process is pivotal in determining the success of a brand. But what exactly is product positioning, and how can it be executed effectively?
This blog covers the meaning and types of product positioning, examples, and strategies to create a winning product positioning map.
What is Product Positioning?
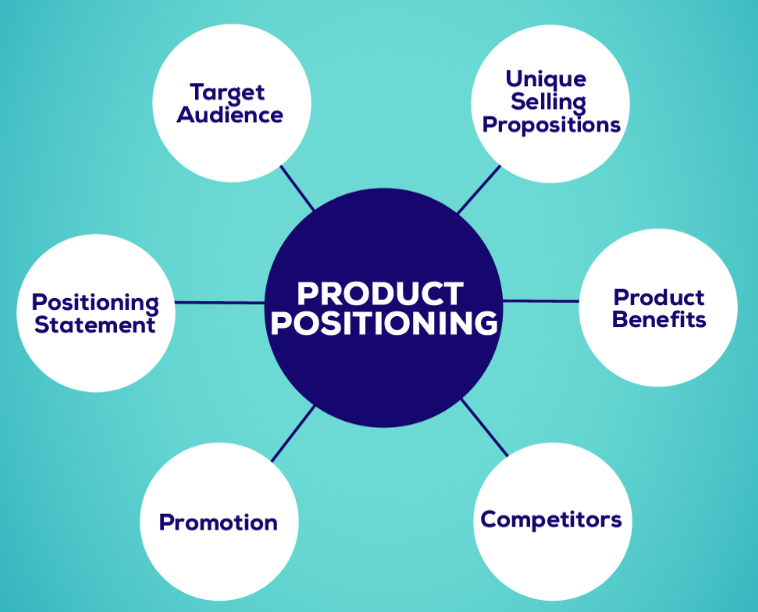
Product positioning is critical for a successful marketing strategy. It creates a unique image of a product and distinguishes it from competitors. It communicates how your product solves customer problems and stands out from competitors. In a crowded market, product positioning is essential to creating a unique identity for your product.
Product positioning involves highlighting the product’s unique features, benefits, and value proposition to differentiate it from competitors. The primary goal of product positioning is to influence consumer purchasing behavior by responding to the needs of the target market.
Effective product positioning enables businesses to establish a competitive advantage, enhance brand recognition, and increase sales.
ALSO READ: How to Craft Effective Brand Survey Questions? The Different Types of Product Positioning

Value-Based Positioning
Value-based positioning focuses on providing customers with a high-quality product that delivers superior value.
This approach typically involves targeting a premium market and charging a higher price point. Some companies that use value-based branding include Apple, Mercedes-Benz, and Rolex.
Benefit-Based Positioning
Benefit-based positioning focuses on highlighting the specific benefits that a product offers to customers.
This strategy works best once the item has distinctive characteristics that set it apart from rivals. Examples of benefit-based positioning companies include Nike, Subway, and Google.
Competitor-Based Positioning
Competitor-based positioning involves comparing a product to its competitors and positioning it as superior in some way.
This strategy may work well when a product has a definite edge over rivals in quality, performance, or cost. Numerous brands, including Coca-Cola and McDonald’s, use competitor-based branding techniques.
User-Based Positioning
User-based positioning focuses on the specific needs and desires of the target market. This approach involves understanding the target customer’s demographics, psychographics, and behavior patterns and positioning the product accordingly.
Examples of companies that use user-based positioning include Procter & Gamble, Ford, and Airbnb.
ALSO READ: 10 Steps to Conduct a Successful Brand Audit Product Positioning Examples
Apple
Apple is a perfect example of value-based positioning. The business has established itself as an exemplary brand that provides outstanding innovation, design, and quality.
The hallmarks of Apple products are high performance, sleek style, and an easy-to-use user layout. This positioning is reflected in Apple’s pricing strategy, which sees the company asking for a premium for its goods.
Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola is an example of competitor-based positioning. Due to its superior taste and recognizable brand, the business has established itself as the market frontrunner in the soft drink sector.
Coca-Cola’s marketing strategy is to forge emotional bonds with its consumers and present its product as a sign of joy and community.
Nike
Nike is an example of benefit-based positioning. The business has established a reputation as a supplier of high-performance athletic equipment that aids competitors in reaching their objectives.
The key component of Nike’s marketing approach is emphasizing the distinctive advantages of its products, such as their toughness, comfort, and style.
Airbnb
Airbnb is an example of user-based positioning. The business has established itself as a supplier of distinctive and genuine travel encounters tailored to meet travelers’ requirements and preferences.
Airbnb’s marketing strategy focuses on creating emotional connections with its customers and positioning its product as a way to explore new places and cultures.
Product Positioning Template for Creating a Strong Brand Identity
- Identify Your Target Market
The first step in creating a product positioning strategy is identifying your target market. It involves understanding your customers’ demographics, psychographics, and behavior patterns.
- Identify Your Unique Value Proposition
The next step is to identify your unique value proposition. It involves understanding what sets your product apart from competitors and how it delivers value to customers.
- Create a Positioning Statement
Once you identify your target market and unique value proposition, you can create a positioning statement. This statement should be a concise summary of your product’s positioning and the benefits of using it. The position statement must be straightforward, clear, and concise.
- Create a Product Positioning Map
A product positioning map visually represents your product’s positioning relative to competitors. This map can help you identify areas where you can differentiate your product and target specific market segments.
- Test Your Product Positioning
Once you have developed your product positioning strategy, testing it with your target market is essential. Gathering input and refining your positioning can be accomplished through surveys, focus groups, and other forms of market research.
ALSO READ: Emotional and Rational Branding: Two Sides of the Same Coin? Product Positioning Map: An Effective Tool for Product Development
A product positioning map is a tool that visually represents how products are positioned in the market. It allows businesses to understand how their product compares to competitors’ products and helps identify opportunities for improvement.
To create a product positioning map, businesses must identify the key factors customers use to evaluate products in their market. The variables include:
- Price
- Performance
- Dependability
- Innovation
- Client Support
Once these key factors are identified, businesses can plot their products and their competitors’ products on a two-dimensional graph. Each axis represents a different factor.
The resulting map shows how the product compares to competitors’ products regarding these key factors.
Conclusion
In marketing, product positioning is crucial for differentiating companies from their rivals and grabbing the attention of their target market. Develop effective positioning strategies that promote growth and connect with customers.
It is crucial to have knowledge of various product positioning types, learn from successful examples, and use a positioning template as a foundation. Businesses can then successfully modify their products to meet their client’s unique requirements and preferences.
Not Sure Where To Begin?
Explore our solutions to discover what is most important to your customers,
clients, and prospects. And best of all – it doesn’t take any coding!
Free Trial • No Payment Details Required • Cancel Anytime