Descriptive research, as the name specifies, describes the scenario or case of a specific study. This research design is purely based on a theoretical foundation where the individual gathers data, analyzes, prepares, and then presents it for decisions.
We will define descriptive research, explain its methodology, and weigh the benefits and drawbacks of this method.
A Brief Overview of Descriptive Research
Descriptive research is the most generalized form of research design. It usually covers questions such as:
- Do customers of a business prefer a product?
- What are the most critical genetic, behavioral, and physical differences between products?
- How common is a certain disease in a population?
Essentially, descriptive research entails amassing numerical and organized information that may be utilized to evaluate the study’s subject’s inherent, uncontrolled factors.
One of the most significant contrasts between descriptive research is that descriptive research does not manipulate or alter factors. Instead, variables are just named, observed, and measured as a foundation for future research. It helps to get a thorough grasp of the research issue to answer it correctly with the data collected from descriptive research.
Generally, cross-sectional studies are used to accomplish the descriptive approach of the investigation. An observational study that involves collecting data at the individual level on many variables is known as a cross-sectional study. Researchers can use descriptive methods to examine changes in variables over time and identify patterns, allowing them to compare variables.
Comparing numerous components and how different populations respond to other variables may be accomplished through descriptive research. As well as identifying the subject’s characteristics, it can also be used to determine their gender. For example, it can include qualities like opinion, attributes, conduct, etc., to confirm or verify current circumstances. When judging the validity of an existing condition, descriptive research may be helpful because it requires a deep look at every variable before concluding.
Related: A Microscopic Introduction To Stratified Random Sampling
Methodologies Of Conducting Descriptive Research
Three primary strategies are used to conduct descriptive research are:
- Surveys
- Case studies
- Observations
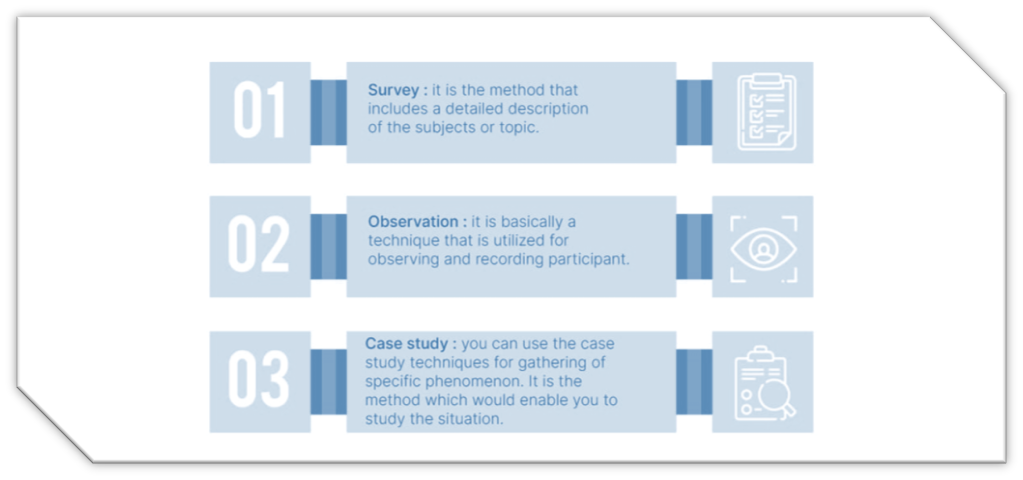
- Surveys are a cost-effective way of collecting data as they can be conducted through digital and non-digital media, such as email, websites, and phone surveys. Survey analysis will help comprehend a place’s demographics or gauge public opinion on social or political issues.
Check out SurveyPoint if you are seeking a survey companion to help create surveys that users are excited to fill out. Pick from a variety of professionally designed, editable survey layouts. - The case study method requires an in-depth examination of individuals or groups. Case studies need specific data on a well-defined topic instead of amassing vast data to identify connections and trends. Therefore, this approach tends to describe the varied characteristics of a single subject rather than to explain generalizable facts.
Case studies help academics create hypotheses that can extend the field of evaluation while investigating the phenomena observed. In this strategy, researchers watch subjects in their natural surroundings from a distance and, as a result, do not affect the examined variables. As a result, they can collect data on investigated behaviors and features without relying on respondents to provide accurate and truthful answers.
- The observational approach is believed to be the most acceptable descriptive research strategy. This strategy includes both qualitative and quantitative data collection.
Advantages
Let’s begin with the advantages of descriptive research. Among the data-gathering methods used in the descriptive analysis are case studies, observational data, and surveys.
- It is fast and cost-efficient since the descriptive research design often incorporates questionnaires. Through this, data can be obtained from a huge sample size in a timely and cost-effective manner.
- Comprehensive descriptive research typically combines quantitative and qualitative research, providing a complete understanding of the search issue and having high external validity.
- Neither the context of the respondents’ lives nor the factors are altered during the study. Hence the results of descriptive research tend to have high external validity.
Disadvantages
- Due to the lack of explanation for the studied phenomena, descriptive research cannot be used to evaluate or validate the research question.
- The approach lacks reliability. If the research topic isn’t well-thought-out, the data collected might not be completely reliable. As a result, it is harder to do a reliable investigation.
- Descriptive research depends on people’s responses, primarily when surveys are conducted. False feedback may occur, compromising the quality of the collected data and, eventually, the study results due to sampling errors.
- The descriptive research method often employs random sampling when picking a sample group. Randomness may lead to sampling error, leading to unreliable and wrong results if the sample group isn’t representative of the whole population.
Learn to work smarter, not harder!
Explore our solutions that help researchers collect accurate insights, boost ROI, and retain respondents.
Free Trial•No Payment Details Required•Cancel Anytime
Kultar Singh – Chief Executive Officer, Sambodhi