Surveys are one of the most commonly used data collection methods in research.
They have come a long way thanks to the introduction of technology. Surveys have seen everything from face-to-face to telephonic to online mediums such as emails or feedback forms.
Each survey data collection method has advantages and disadvantages, but they always provide you with invaluable data.
However, despite their positives, they also bring in unwanted errors, which can screw up your estimates and render your research useless.
The most prominent of these errors are sampling errors.
These little villains sneak into your idyllic world and sow seeds of chaos and doubt. They can take this to the point where you’ll start doubting the credibility of your entire outcome.
So, how do you avoid these errors? Or, at the very least, minimize their extent?
Well, you’re in the right place!
In this blog, we’ll understand sampling errors, why they matter, and how you can beat the odds to get precise and reliable results.
Grab a cup of coffee or tea, and let’s get started!
What Are Sampling Errors, and Why Do They Matter?
Before we jump into what is a sampling error in research, you need a basic idea about sampling and how to use it in survey research. (However, if you’re aware of it, feel free to skip this section.)
When conducting a survey, you’re usually interested in an audience much bigger than you can reach. But you can’t possibly survey your entire audience.
So how can you make up for this?
The answer is: to take a representative sample.
This sample is a subset of the larger population you want to study.
Now that you’re ready to start your survey, you must follow some of the best survey sampling practices.
The first thing you should do is choose the right sample size. It ensures that your sample size will adequately represent the remaining population.
If your sample size is too large, your efforts will be wasted with nothing to show for them. Whereas if your sample size is too small, it can’t represent the population. Either case will lead to inaccurate results.
However, there’s more to sampling than just getting the appropriate sample size. You should also have a basic knowledge of sampling and non-sampling errors.
Understanding these errors will allow you to keep your research problem-free and accurate, which brings us to the next part.
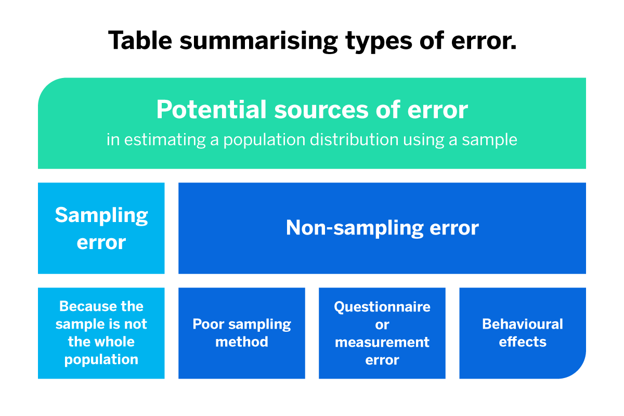
Sampling Errors Vs. Non-Sampling Errors
Surprisingly, the term ‘sampling error’ does not mean errors made by researchers or while working with a sample.
Mistakes like choosing the wrong audience and failing to anticipate that participants will either not respond, self-select or get biased are examples of non-sampling errors.
Sampling Error Definition
On the other hand, sampling errors are random differences between the characteristics of a sample population and those of the entire population.
These inevitable errors arise due to the limited sample size. As the OECD states, you’ll never be able to perfectly represent the actual population, as it is larger than the sample size and more complete.
Simply put, sampling errors are not human errors and cannot be avoided. You also cannot measure the degree of sampling error in a study.
However, you can reduce sampling errors by implementing good practices.
Non-sampling Error Definition
Non-sampling errors can occur even when you’re not sampling.
These errors occur when there are issues with the sampling method or how a survey is designed and conducted. Any errors other than sampling errors are non-sampling errors.
Types of Sampling Errors
Let’s take a look at the different sampling error types and their examples:
Population-Specific Error
This error occurs when the researcher isn’t sure who his target audience is.
For example, imagine a survey about kids’ toys.
Who’s the right person to survey?
Possibly both the parents, or perhaps only the mother or the child. The parents will have the final say, but the kids will heavily influence this decision.
You can avoid this error by clarifying what you hope to achieve and who will best help you. The recognized audience will then be your target audience.
Selection Error
This error occurs when people volunteer to participate in the survey. It is likely that the volunteers feel strongly about the subject and want their voices heard. However, this leaves out people who are indifferent or against the issue.
You can avoid this error by implementing better data collection methods. Also, consider taking extra steps to encourage participation among your respondents.
Sample Frame Error
This error occurs when the researchers target the wrong sample population. Inaccurate sample data fails to accurately represent the entire population.
Take the 1936 U.S. presidential election as an example.
The researchers took a sample audience from car registrations and telephone directories. In 1936, only a few rich individuals owned cars or telephones. And most of them who did were Republicans!
The results predicted a Republican victory, which later proved wide of the mark.
You can avoid this error by using multiple survey method types, increasing the audience size, and ensuring that most respondents represent the rest of the population.
Non-response Error
A non-response error occurs when potential respondents refuse to respond or are not reachable. This leads to a smaller non-random sample, which misrepresents the rest of the population.
You can avoid this error by using multiple survey method types and follow-up surveys.
How to Reduce Sampling Errors?
Identifying sampling errors isn’t enough; you need to reduce their numbers. Here are a few ways that can help you with that:
Increase sample size
As the sample size increases, it gets closer to the actual population. Thus, it is precise and contains far fewer deviations than a smaller sample size.
Understand Your Audience
Research and study your audience. Make sure you know which demographics you target and use your products or services to target the right ones.
Use Cluster Sampling
Cluster sampling consists of dividing the population into clusters or groups.
You then select a random sample of clusters to represent the population. It is a more efficient way of choosing a sample, as it helps reduce sampling errors.
Use Random Sampling
Random Sampling provides everyone in the population with the same chance of being handpicked for the sample. This minimizes bias and increases the representativeness of the sample.
Conclusion
Undoubtedly, surveys are a great tool for researchers and marketers.
However, sampling or non-sampling errors can make your research unreliable and dangerous.
Operating on such research or data can ruin your research or backfire on your business. Hence, you should be smart enough to avoid the above-mentioned errors.
However, if you’re still concerned about such errors and need an extra hand to create surveys, check out Survey Point.
Our interactive and flexible platform helps you create and launch surveys correctly.
Get insights in real-time and transform your data into decisions.