Sampling is a crucial component of research that aids in assembling an accurate representation of the community. A sample is a selected group of people chosen from an expanded population to reflect the traits of the population. Non-probability sampling methods like quota sampling can be used to reliably represent the entire population within specified limits.
The choice of the group in any research study is essential to guaranteeing the generalizability of the findings. Researchers can choose their samples using a variety of selection techniques.
This article will address the quota sampling technique, outline its benefits and drawbacks, and present examples of its application in research.
What is Quota Sampling?
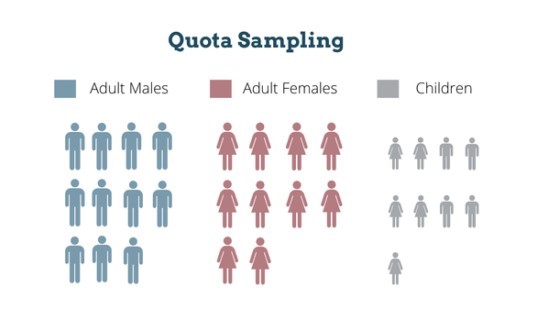
Quota sampling is a non-probability technique used to choose a group that accurately reflects the attributes of a larger community. In quota sampling, the researcher chooses the population based on predetermined quotas or features like age, gender, race, or income.
Although the selection process is not random, the sample is at par to guarantee that every trait is treated equally. To investigate gender-based violence, a researcher might select a sample split 50/50 between men and women for comparison.
Researchers often use quota sampling when resource limitations make it challenging to use a random sampling technique.
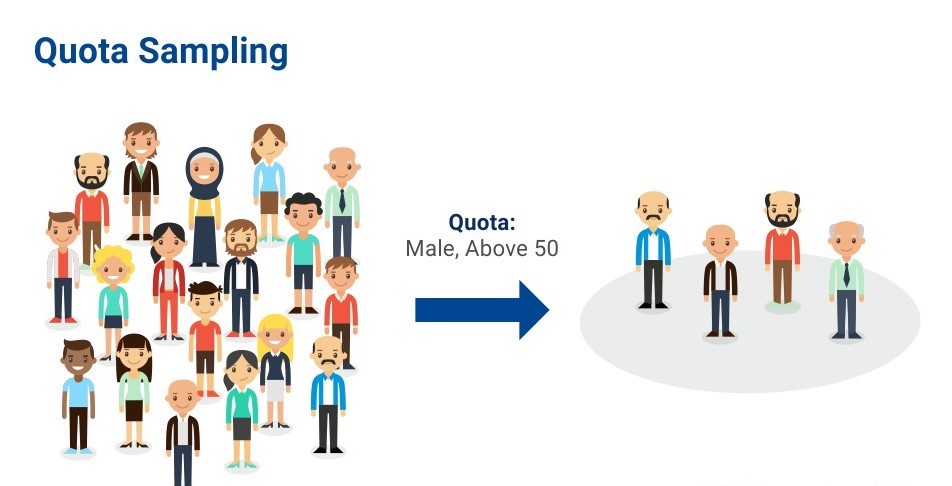
Advantages of Quota Sampling
Researchers who are unable to use probability sampling, use quota sampling. It has several benefits, such as:
- Cost-effective - Although quota sampling does not call for complicated sampling methods, which can be costly, it is an economic sampling strategy. The researcher doesn’t need to contact every community member, which can also take time.
- Practical - When a researcher has little time or money, quota sampling is a fast and effective sample selection method.
- Diversity - Even if the populace is broad and varied, quota sampling guarantees that the sample accurately reflects that diversity. You can check the selection to ensure it represents a wide range of ages, gender, ethnicity, and other pertinent characteristics.
- Specific subgroups - When the study topic calls for including particular subsets in the sample, like minorities or low-income groups, quota sampling is helpful.
- Convenience - This technique is convenient for researchers since it does not require a comprehensive population list. Instead, researchers can calculate the quotas using easily accessible data, like census data.
Disadvantages of Quota Sampling
While quota sampling has numerous benefits, it also has some drawbacks, such as:
- Bias - The researcher’s selection of subjects in quota sampling can introduce bias, as they are not choosing randomly. A biased sample may result from the researcher unintentionally selecting more approachable or willing individuals to engage.
- Non-random – Since it uses a non-random sampling technique, the sample might not accurately reflect the entire community.
- Limited generalizability – Quota sampling doesn’t offer a comprehensive sample of the community, restricting the generalizability of the research’s insights. The findings might not be relevant to other groups or situations.
- Difficulty in selecting quotas – It can be difficult, particularly if the researcher is unsure how the distribution of demographic characteristics will turn out.
- Sampling error – If the quotas don’t match the characteristics of the community, quota sampling may result in sampling error. The sample may not accurately reflect the population if the quotas are inaccurate.
Common Misconceptions About Quota Sampling
Despite quota sampling’s value in research, there are a few widespread fallacies.
- One typical misunderstanding is that stratified sampling and quota sampling are interchangeable.
- Both methods segment the community into subsets according to different traits. Still, stratified sampling chooses individuals at random from each subgroup. Comparatively, quota sampling entails actively looking for people who meet the quotas.
- An additional fallacy is an idea that quota selection is always biased. However, quotas established incorrectly can result in biased samples. But this happens only sometimes if participants are chosen randomly within each quota.
ALSO READ: A Primer On Stratified Sampling: Definition, Benefits, And Examples Quota Sampling Examples
Source – mathstopia.net
Numerous research studies employ quota sampling. Here are a few instances:
- Researchers are conducting a study to determine the feelings of young people regarding climate change. Using a quota sampling technique, the researcher consists of equal numbers of men and women between the ages of 18 and 25.
- A political researcher wishes to determine who will vote in a forthcoming election. To guarantee that the sample contains an equivalent number of enrolled Democrats, Republicans, and Independents.
- A market research company wishes to investigate how consumers shop. A quota sampling technique guarantees that the sample contains a proportionate number of customers from various income categories.
- A health organization intends to survey the incidence of a specific disease in a nation. To guarantee that the sample accurately reflects the diversity of the population, the organization employs census data. It establishes the quotas for various age groups, genders, and geographic areas.
ALSO READ: Studying Population Data: Meaning, Characteristics & Importance How to Implement Quota Sampling in Research?
Researchers must decide which characteristics are crucial to their research, such as age, gender, etc., before using quota sampling. Then, establish quotas for each attribute based on their distribution within the target group.
Finally, using a variety of techniques like internet surveys, telephone interviews, or in-person discussions, experts must proactively seek out people who meet the quotas.
Conclusion
Quota sampling is a helpful research technique to ensure that the sample studied is accurate to the community of interest. Researchers can guarantee that their sample represents the same dispersion of traits as the community being studied. This is established for quotas of particular characteristics and constantly pursuing individuals who fall within these same quotas.
Although quota sampling has some drawbacks, such as the possibility of partiality and the time and money required for enrollment. For researchers in various fields, it is an invaluable tool because of its advantages for research.
Not Sure Where To Begin?
Explore our solutions to discover what is most important to your customers,
clients, and prospects. And best of all – it doesn’t take any coding!
Free Trial • No Payment Details Required • Cancel Anytime




